基于Android 10.0的源码剖析, 站在Luoshengyang/Innost/Gityuan肩膀上.
本文分析Native层ServiceManager获取过程.
0.文件结构
frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
frameworks/native/include/binder/IServiceManager.h
frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/binder/BpBinder.cpp
1.时序图
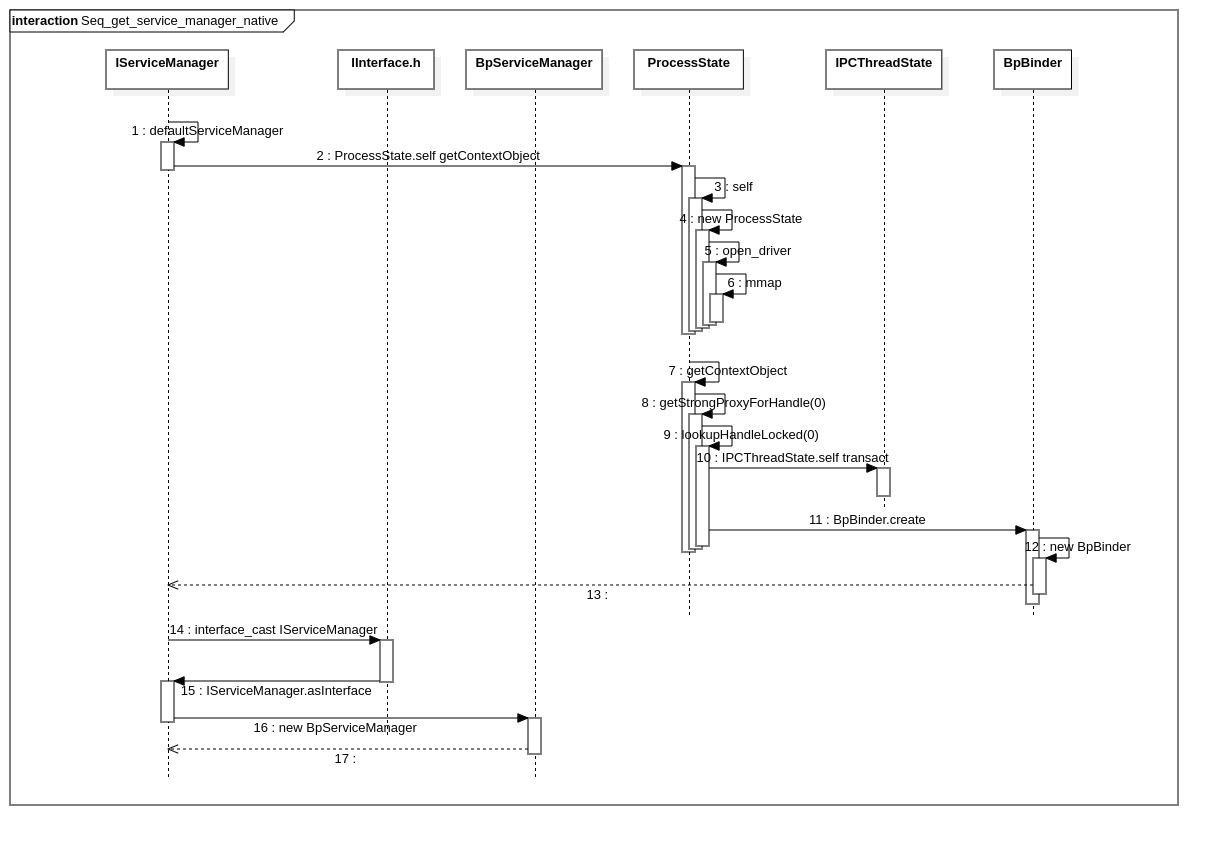
2.入口函数
[ -> frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp ]
// IServiceManager.defaultServiceManager()
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != nullptr) return gDefaultServiceManager;
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
while (gDefaultServiceManager == nullptr) {
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(nullptr));
if (gDefaultServiceManager == nullptr)
sleep(1);
}
}
return gDefaultServiceManager;
}
3.获取BpBinder对象
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(nullptr)
上一篇文章 ServiceManager获取过程–Java层 已经讲解:
http://mouxuejie.com/blog/2020-01-05/get-service-manager-java/
4.获取BpServiceManager对象
【第3节】获取到了BpBinder对象, 然后调用interface_cast< IServiceManager >转换为BpServiceManager对象.
那么具体是怎么转换的呢? 我们找到interface_cast方法的实现.
4.1 interface_cast
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h ]
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
}
根据interface_cast方法的实现, 可知interface_cast< IServiceManager >等价于IServiceManager::asInterface
4.2 IServiceManager::asInterface
按照正常思路, 我们找IServiceManager::asInterface的实现.
然而在IServiceManager.cpp和IServiceManager.h文件中都没找到对应的实现.
再认真看代码, 发现IServiceManager.h中有代码:
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IServiceManager.h ]
// 接口声明
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager)
IServiceManager.cpp中有代码:
[ -> frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp ]
// 接口实现
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager")
从字面含义, 分别是接口声明和接口实现的定义.
我们看下面代码具体实现.
4.3 模板方法
4.3.1 DECLARE_META_INTERFACE
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h ]
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \
public: \
static const ::android::String16 descriptor; \
static ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> asInterface( \
const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& obj); \
virtual const ::android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
I##INTERFACE(); \
virtual ~I##INTERFACE(); \
static bool setDefaultImpl(std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> impl); \
static const std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE>& getDefaultImpl(); \
private: \
static std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> default_impl; \
上面代码也就是增加了几个接口方法, 其中包含asInterface方法.
4.3.2 IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h ]
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \
const ::android::String16 I##INTERFACE::descriptor(NAME); \
const ::android::String16& \
I##INTERFACE::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
return I##INTERFACE::descriptor; \
} \
::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \
const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& obj) \
{ \
::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> intr; \
if (obj != nullptr) { \
intr = static_cast<I##INTERFACE*>( \
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
I##INTERFACE::descriptor).get()); \
if (intr == nullptr) { \
intr = new Bp##INTERFACE(obj); \
} \
} \
return intr; \
} \
std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::default_impl; \
bool I##INTERFACE::setDefaultImpl(std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE> impl)\
{ \
if (!I##INTERFACE::default_impl && impl) { \
I##INTERFACE::default_impl = std::move(impl); \
return true; \
} \
return false; \
} \
const std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE>& I##INTERFACE::getDefaultImpl() \
{ \
return I##INTERFACE::default_impl; \
} \
I##INTERFACE::I##INTERFACE() { } \
I##INTERFACE::~I##INTERFACE() { }
上面代码是接口方法的具体实现, 我们可以看到INTERFACE::asInterface的函数实现.
我们可以得出, IServiceManager::asInterface的实现为:
sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
sp<IServiceManager> intr;
if (obj != nullptr) {
// BpBinder.queryLocalInterface返回null
intr = static_cast<IServiceManager*>(
obj->queryLocalInterface(IServiceManager::descriptor).get());
if (intr == nullptr) {
// 创建BpServiceManager对象
intr = new BpServiceManager(obj);
}
}
return intr;
}
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h ]
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline sp<IInterface> BnInterface<INTERFACE>::queryLocalInterface(
const String16& _descriptor)
{
if (_descriptor == INTERFACE::descriptor) return this;
return nullptr;
}
4.4 BpServiceManager实例化
4.4.1 BpServiceManager
[ -> frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp ]
explicit BpServiceManager(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl)
{
}
4.4.2 BpInterface< IServiceManager >
[ -> frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h ]
template<typename INTERFACE>
class BpInterface : public INTERFACE, public BpRefBase
{
public:
explicit BpInterface(const sp<IBinder>& remote);
protected:
typedef INTERFACE BaseInterface;
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
};
4.4.3 BpRefBase
BpRefBase::BpRefBase(const sp<IBinder>& o)
: mRemote(o.get()), mRefs(nullptr), mState(0)
{
extendObjectLifetime(OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK);
if (mRemote) {
mRemote->incStrong(this); // Removed on first IncStrong().
mRefs = mRemote->createWeak(this); // Held for our entire lifetime.
}
}
Native层BpServiceManager实例化时, mRemote指向BpBinder对象.
Java层ServiceManagerProxy实例化时, mRemote指向BinderProxy对象.
两者思路一模一样.
5.总结
Native层 ServiceManager获取过程分为2步:
1.先判断是否有已创建的实例gDefaultServiceManager, 若有则直接返回, 否则新建一个
2.创建ServiceManager实例过程:
(1) ProcessState::self()->getContextObject 获取BpBinder对象(和前一篇文章Java层获取一模一样)
ProcessState::self()创建ProcessState对象open_driver打开binder驱动,设置binder版本号和最大线程数15mmap执行binder mmap内存映射,分配一块虚拟内存,用来接收事务getContextObject获取BpBinder对象.调用getStrongProxyForHandle(0). 首先通过lookupHandleLocked方法查询mHandleToObject顺序列表中是否存在handle=0的BpBinder, 若不存在则通过BpBinder::create创建. 当然在创建BpBinder之前需要保证上下文管理器context manager准备就绪, 具体方法就是向binder驱动发送IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION指令, 看返回结果是否正常.
(2) interface_cast< IServiceManager > 获取BpServiceManager对象
interface_cast的关键就是模板方法DECLARE_META_INTERFACE和IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE.
具体过程是先通过BpBinder.queryLocalInterface查询本地是否包含BpServiceManager对象, 结果返回null.
new BpServiceManager创建一个新对象.