1、自定义View
(1)整体结构及工作流程
(2)measure
(3)layout
(4)draw
2、measure过程
(1)MeasureSpec(measureSpec/mode/size)
(2)父View宽高的测量方法
(3)子View宽高的测量方法
3、layout过程
(1)left/top/right/bottom含义
(2)left/top/right/bottom计算
4、draw过程
(1)绘制顺序
5、源码举例
(1)LinearLayout
(2)ListView
(3)ScrollView
6、参考文档
1、自定义View
(1)整体结构及工作流程
Activity、Window、DecorView之间的关系:
Activity:相当于一个Controller,具备生命周期。
Window:相当于窗口,是视图的承载器,PhoneWindow是唯一实现类。
DecorView:顶级View,是一个Framelayout,包含StatusBar、TitleBar+ContentView、NavigationBar三个部分。
StatusBar是状态栏;
TitleBar对应各种ActionBar;
ContentView对应R.id.content,setContentView设置的View被添加到R.id.content对应的View上,可通过findViewById(android.id.content)得到ContentView,findViewById(android.id.content).getChildAt(0)得到设置进去的View;
NavigationBar是虚拟按键。
延伸:沉浸式状态栏本质是将状态栏、导航栏隐藏,实现应用界面全屏化。 状态栏及导航栏相关知识小结
ViewRoot:实现类是ViewRootImpl,它是连接WindowManager和DecorView的纽带,View的三大流程是通过ViewRoot来完成的。
View的工作流程:
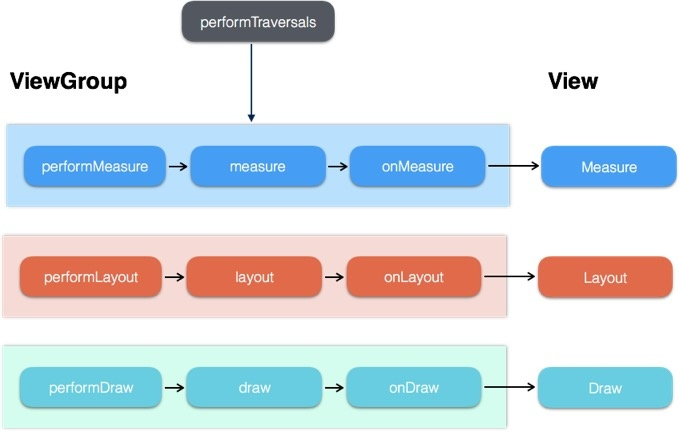
- 最先从ViewRoot.performTraversals()方法开始
- DecorView的绘制:调用DecorView的performMeasure,performLayout,performDraw三个方法。DecorView的measure顺序:performMeasure -> measure -> onMeasure;DecorView的layout顺序:performLayout -> layout -> onLayout;DecorView的draw顺序:performDraw -> draw -> onDraw。然后onMeasure/onLayout/onDraw又会调用child.measure()/child.layout()/child.onDraw()将这个过程传给child。
- 子View的绘制:measure过程 measure -> onMeasure;layout -> onLayout;draw -> onDraw
- 依次往下传递。
measure过程:得到所有View体系的宽高
layout过程:得到所有View的坐标
draw过程:绘制所有View
关于requestLayout()/invalidate():
requestLayout()会调用到ViewRoot.performTraversals(),触发measure、layout和draw过程;postInvalidate()和invalidate()会出发当前View的draw过程,但是前者在非UI线程,后者在UI线程调用。
Android View 深度分析requestLayout、invalidate与postInvalidate
整个过程的简略版代码,以LinearLayout为例:
(2)measure
measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)做的事情:
- 保存widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec
- 调用onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)方法
onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)做的事情:
- 调用child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec)测量子View的宽高
- 得到当前View的总宽高,并调用setMeasuredDimension(totalWidth, totalHeight)保存总宽高
setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight)做的事情:
- 保存当前View的总宽高
具体代码如下:
//LinearLayout
@Override
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
...
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int totalWidth = ...;
int totalHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
totalHeight += child.getMeasureHeight();
}
...
setMeasuredDimension(totalWidth, totalHeight);
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
private void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
}
(3)layout
layout(int l, int t, int r, int b)做的事情:
- 保存当前View的坐标
- 调用onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b)方法
onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)做的事情:
- 计算子View的坐标
- 调用child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom)将子View的坐标传给子View
具体代码如下:
//LinearLayout
@Override
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
mLeft = l;
mTop = t;
mRight = r;
mBottom = b;
...
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
...
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
...
childLeft = ...;
childTop = ...;
childRight = childLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth();
childBottom = childTop + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
}
}
(4)draw
draw(Canvas canvas)做的事情:
- 调用drawBackground(canvas)绘制背景
- save canvas‘ layers
- 调用onDraw(canvas)绘制内容
- 调用dispatchDraw(canvas)绘制子View
- 绘制fade effect和restore layers
- 调用onDrawScrollBars(canvas)绘制滚动条
onDraw(canvas)做的事情:
- 绘制当前View的内容
dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas)做的事情:
- 调用child.draw(canvas)绘制子View
具体代码如下:
//LinearLayout
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
drawBackground(canvas);
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers(非必需)
// Step 3, draw the content
onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers(非必需)
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
}
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
drawChild(canvas, child);
}
}
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
2、measure过程
(1)MeasureSpec(measureSpec/mode/size)
measureSpec:32位的int值,高2位代表mode,低30位 代表size。
mode是测量模式,包括:
UNSPECIFIED:父View对当前View没啥限制,当前View可以是任意大小
EXACTLY:父View决定了当前View的精确大小
AT_MOST:当前View最高可以到某个大小
size指某种测量模式下的规格大小。
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}
(2)父View宽高的测量方法
根据父View中子View的布局样式,可能受子View的宽高影响。
如布局为水平方向,则宽度为子View宽度的累加;布局为垂直方向,则高度为子View高度的累加。其它根据实际情况而定。
宽高计算出来之后之后,调用setMeasuredDimension()设置宽高的值。
宽高的计算过程中,可能需要累加各种padding、margin、分割线之类的。
(3)子View宽高的测量方法
测量子View的方法measureChild:
(1)先计算出子View的measureSpec,即childMeasureSpec
(2)再根据child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec)测量子View的大小
测量完成之后,可以根据getMeasuredWidth()和getMeasuredHeight()得到测量出来的宽高值
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
childMeasureSpec的计算:
由parentMeasureSpec和childDimension共同约束。
childDimension是LayoutParams中的width和height,要得到childMeasureSpec,需要先得到childSpecMode和childSpecSize。
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//父View的mode和size
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//子View最大大小(父View的大小-内边距)
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
//有精确值的情况
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//填满父容器,而父容器又是一个精确值,因此子View也是精确模式
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//内容自适应,而父容器又是一个精确值,因此子View有最大值
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
//有精确值的情况
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//填满父容器,而父容器又是最大值模式,因此子View也是最大值模式
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//内容自适应,而父容器又是最大值模式,因此子View也是最大值模式
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
//有精确值的情况
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//填满父容器,而父容器是未指定模式,因此子View也是未指定模式
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//内容自适应,而父容器是未指定模式,因此子View也是未指定模式
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//根据mode和size得到measureSpec
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
前面举的例子是LinearLayout,它复写了onMeasure方法。
如果不复写onMeasure()的话,当前View的默认宽高的实现如图:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
//默认大小,由自身的最小宽高和自身的measureSpec共同决定
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
//建议的最小宽度,由layout:minWidth属性和mBackground的最小宽度共同决定
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
3、layout过程
(1)left/top/right/bottom含义
是相对坐标,相对于父View的坐标。
(2)left/top/right/bottom计算
无非是结合各种padding、margin、divider来计算。
还是以LinearLayout为例(简化版):
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
//父View的内边距
int childTop = mPaddingTop;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//分割线
childTop += mDividerHeight;
//topMargin
childTop += lp.topMargin;
childBottom = childTop + childHeight;
//父View的内边距和子View的leftMargin
childLeft = mPaddingLeft + lp.leftMargin;
childRight = childLeft + childWidth;
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
}
}
4、draw过程
(1)绘制顺序
上面已经介绍了。
5、源码举例
自定义View的套路:
(1)复写的方法无非onMeasure、onLayout、onDraw/dispatchDraw,根据情况,有可能复写其中的某几个。
(2)onMeasure方法中调用child.measure()测量子View大小,并计算当前View的大小。如果当前View的大小是默认计算方式,则不需要复写该方法。
(3)onLayout方法中调用child.layout()设置子View的坐标位置,并保存当前View的位置坐标。
(4)onDraw绘制当前View的内容,dispatchDraw绘制子View的内容,一般不复写dispatchDraw。
下面几个View源码的套路都差不多,ListView在该套路基础上增加了Recycler复用机制。
(1)LinearLayout
(2)ListView
(3)ScrollView
可以参考FlowLayout的源码:https://github.com/Mr-YangCheng/ForAndroidInterview/blob/master/android/Android%20%E8%87%AA%E5%AE%9A%E4%B9%89ViewGroup%E5%85%A5%E9%97%A8%E5%AE%9E%E8%B7%B5.md
6、参考文档
(1)setContentView 背后那些事儿
(2)Window、Activity、DecorView以及ViewRoot之间的关系
(3)View测量、布局及绘制原理
